How to Configure Network Settings on CentOS 7 Using the Terminal
How Network Interface Naming Works?
RHEL introduced its new naming convention for network interfaces in version RHEL 6. However, the feature was enabled by default only with version 7, which meant that eth0 and eth1 were no more.
The names are now defined by a group of factors (device type, adapter, port/ID, and so on).
Based on the device type, the network interface name can start with:
en – Ethernet interface
wl – Wlan interface
ww – Wwam interface
sl – Serial line IP (slip)Configuring a Static IP
You can set up a static IP via command line by modifying the network script of the interface.
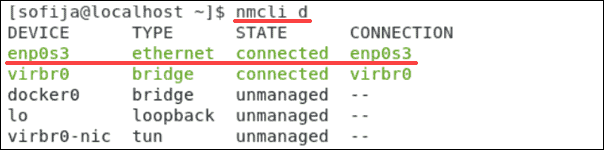
- First, find the name of the network interface you want to change using the network manager command-line tool. Prompt the system to list all network devices, along with network details:
nmcli d
In our example, we will change the configuration for the first network.
- To do so, open the network’s configuration file by typing the following:
vi /etc/sysconf ig/network-scripts/ifcfg-[network_device_name]
-
A text editor with the network configuration opens.
-
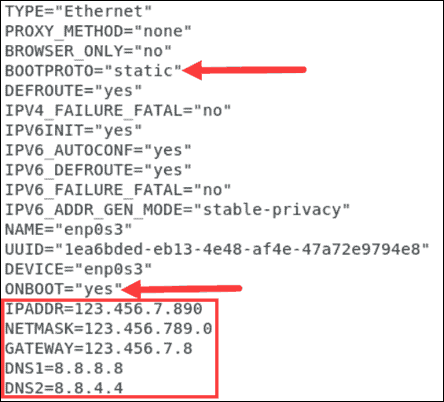
To set a static IP for your network, you need to change the BOOTPROTO line to have the value "static". Also, modify the ONBOOT option to "yes" to enable the network when starting the system.
-
Then, add the following information about your network under the already existing text:
IPADDR=...
NETMASK=...
GATEWAY=...
DNS1=...
DNS2=...
The configuration file should be similar to the example below:
-
Save the file and exit the text editor, returning to the command line.
-
For these changes to take effect, you must restart the network with the command:
systemctl restart
Note: If you don’t have network details (such as the IP address, gateway, and so on), run the command nmcli dev show [network_device_name]. The output displays all the information it has on the network.

You can configure a network for DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) via command line by changing the network configuration.
- Instruct the system to list your network devices with the command:
nmcli d
Find the network you want to configure for DHCP and copy its name.
- Then, open the appropriate configuration file. Use the following command and paste the device name at the end:
vi /etc/sysconf ig/network-scripts/ifcfg-[network_device_name]
-
A text editor with the network configuration opens.
-
The BOOTPROTO line should have the value "dhcp" and change the ONBOOT line to "yes" to enable the network. Also, add network details such as IPADDR, NETMASK, GATEWAY, and DNS.
-
Save the file and exit to return to the command line.
-
Finally, restart the network with:
systemctl restart
How to Configure Network Settings on CentOS 7 Using GUI
To configure your CentOS network interface via GUI, you need to open the Network Manager and modify the configuration according to your needs.
- Open the Network Manager by running the following command in the command line:
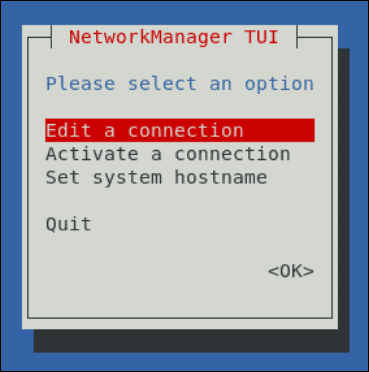
nmtui
- The command prompts the NetworkManager TUI window, which appears as in the image below. Select Edit a connection to view configuration settings.
- Next, choose the network you want to configure.

You can now edit the given connection.

If you want to set the connection to have a static IP address, you can modify the configuration with the Network Manager.
-
First, open the required connection settings. If you have followed the steps outlined in the section above, you should already have the Edit a connection window in front of you.
-
To set a static IP address for the IPv4 configuration, open the drop-down menu next to the name of the appropriate connection.
-
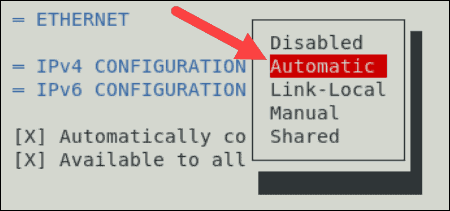
By default, it is set to Automatic. Change the settings to Manual.

- Then, select the Show option for the given network to add the necessary information.

-
Now you can add information related to your connection. This includes the addresses, gateways, DNS servers, and search domains. You don’t have to fill out all the fields.
-
Finally, make sure to enable the option for requiring IPv4 addressing for this connection and automatic connection.
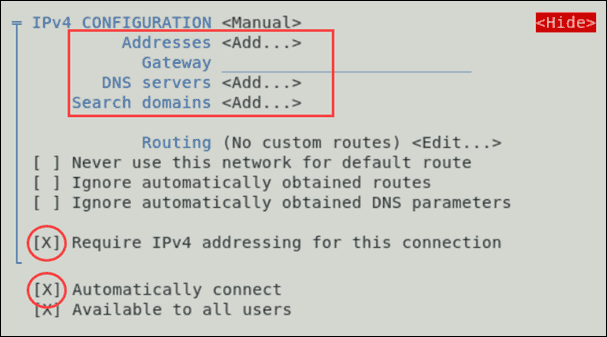
- Select OK and Back to return to the main menu.

-
To configure a network as DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), you need to set the IPv4 configuration settings to Automatic. Configure network for using DHCP on CentOS via GUI.
-
Before you exit out of the Network Manager, make sure to enable automatic connection for the network interface.

-
Select OK to save the changes.
-
Then, exit out of the Network Manages by selecting Back and then Quit.
-
To enable the new configuration, you need to restart the service network by typing the following command in the terminal:
service network restart
Set a System Hostname
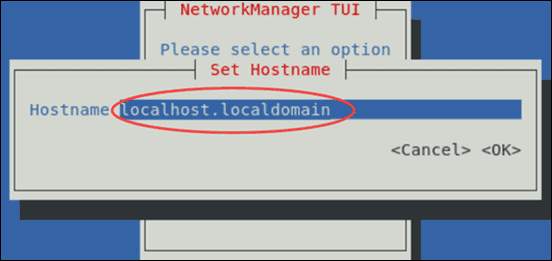
You can also change your hostname using the Network Manager by selecting the Set system hostname option in the main menu.

Type in the new hostname and select OK.
Note: For more information on how to change or set hostname on CentOS, please refer to our tutorials for CentOS 7 and CentOS 8.
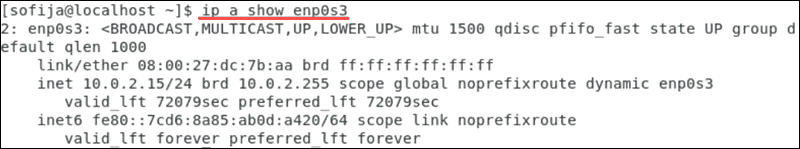
Verify your network is now working with the new settings with the command:
ip a show [network_device_name]
The output will display interface information based on which you can verify if the changes are live. Validate you network settings on CentOS 7.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you should have successfully configured the network settings on your CentOS system. If one method seems too difficult, try another method explained in this article.